How to Undertake a Food Safety Culture Survey
Undertaking a Food Safety Culture Survey
Although many food manufacturers have a comprehensive documented Food Safety Management Systems in place they often lack the tools to be able to evaluate, manage and improve Food Safety Culture within the organisation. A positive attitude towards food safety culture at all levels in conjunction with a robust food safety management system is the key to minimising the risk of producing food that may lead to a food safety issue.
Other consequences identified in having a weak food safety culture is an inability to retain staff. Employee’s express frustration and a sense of powerlessness at work, individuals complain about poor communication and organisations find it difficult to employ good quality personnel.
totrain work with organisations to evaluate and where appropriate create a fundamental change in the organisations food Safety Culture at all levels across all departments. The Food Safety Culture model adopted by totrain is the enlighten 4C Food Safety Culture model.
The 4C Food Safety Culture Model has been developed by Dr Derek Watson of the University of Sunderland specifically for the food manufacturing industry and focuses on the following elements:
Control (Strategy, Leadership, Process and Change)
Co-operation (Responsibility, Empowerment, Teams and Recognition)
Communication (Vision, Norms, Consistency and Feedback)
Competence (Training, Appraisal, Development and Self-belief)
The methodology for undertaking a Food Safety Culture Survey can be defined in the following Food Safety Culture Study Model based on Kirt Lewin change management principles of unfreeze, change and re freeze.
Food Safety Culture Study Model
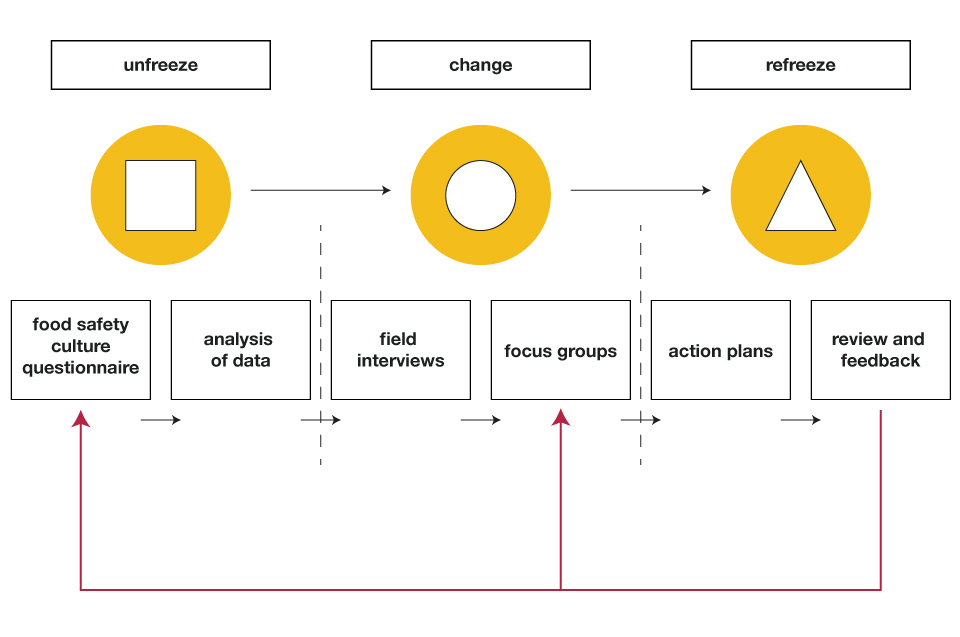
The 6 stages to undertaking a Food Safety Culture Survey
1. Food safety Culture Questionnaire
The enlighten Food Safety Culture Questionnaire structure has adopted positive questions based on the bipolar format to allow the respondent’s intensity of feelings to be determined based on two opposite dimensions, Dislike to Like.
The 4C Food Safety Model measures responses to individual questions using the 5-point Likert Scale covering Strongly Disagree, Disagree, Neutral, Agree and Strongly Agree.
Prior to undertaking the Food safety Culture Survey the company needs to formulate and deliver an effective communications plan to all employees explaining why the Food Safety Study is being undertake, the input expected from each employee and what the company expects to achieve from the Food Safety Culture Survey.
The questionnaire can be distributed electronically, through the enlighten on line culture model or in a hard copy format. Where required questionnaires can be distributed in different languages.
2. Analysis of data
There are three stages to analysis data from a Food Safety Culture questionnaire:
– Quick review
– Editing and cleaning
– Detailed analysis
The enlighten 4C Food Safety model analyses data across the following variables using a average score to allow different variables to be analysed and allocated a risk rating:
- Company
- 4 elements of the enlighten culture model covering Control, Co-operation, Communication and Competency
- Across all levels in the organisation – senior managers, managers/supervisors, operatives and Technical/QA.
- English speaking and non-English speaking
On completion of the data analysis a comprehensive report is generated and presented to Senior Management on the key findings and trends.
3. Field Interviews
Field Interviews and Focus Groups are used as part of the triangulation method to check and establish validity of the survey’s results. The process involves taking the trends and issues raised through the questionnaires and revisiting relevant questions as part of a one to one interview with randomly selected personnel.
The one to one interview also allows the facilitator to obtain anecdotal feedback that can give further insight in to the company culture and also needs to be incorporated into the report to allow further analysis.
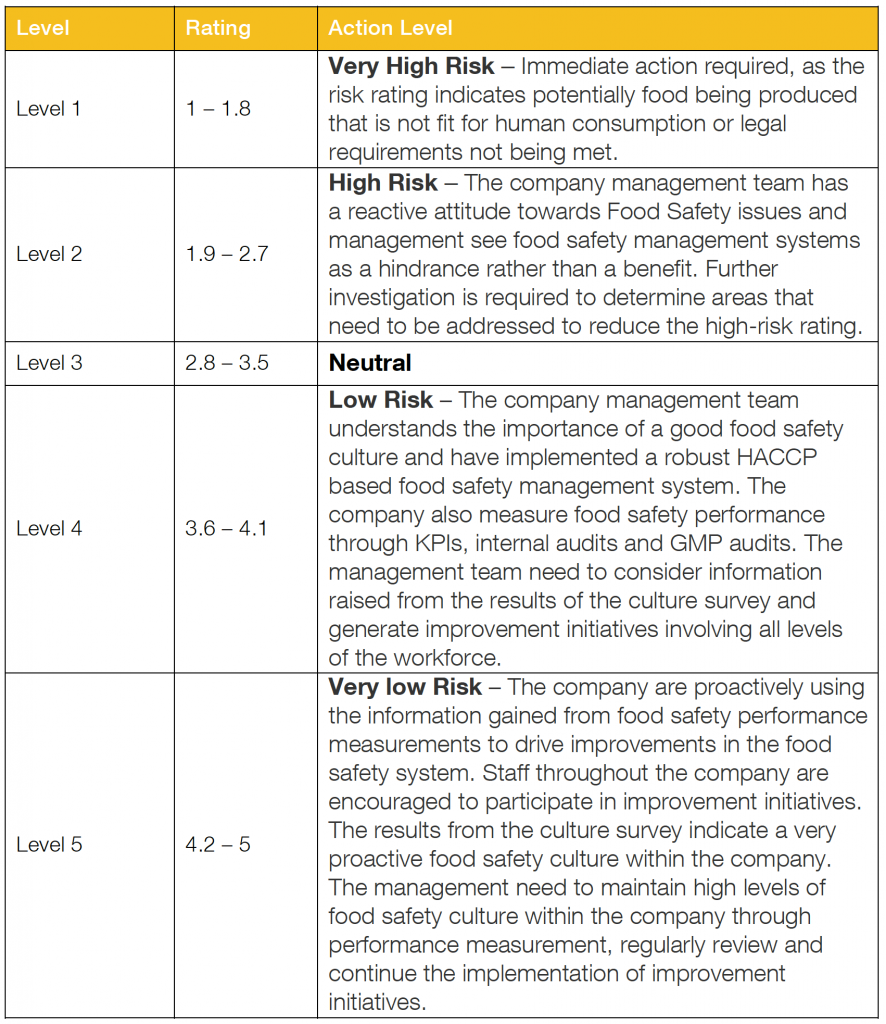
On completion of the field audit the Food Safety Culture Report is updated with the findings from the field audit. It is important to note at this point the Facilitator reviews the average score for each question and a revises the average score to bring in line with the findings from the field audit. The overall average score for the company can then be re calculated and the food safety risk level determined using the enlighten Food Safety Culture Risk Framework.
The frame work provides the following guidance depending on the level of risk:
Food Safety Culture Risk Framework Action Levels
4. Focus Groups
The revised Food Safety Culture report is reviewed by the Senior Management Team and the Facilitator to determine the key points to be covered at the focus group meetings. The focus group comprise of voluntary participants and participants who have be invited.
The focus group will be run by the facilitator who may use one of the following techniques to stimulate debate and provide focus and direction to the group:
- Brain storming
- Field Force Analysis
- Fishbone Diagram
- World Café exercise
The purpose of the focus group is to draw upon participants attitudes, feelings, beliefs, experiences and reactions to the issues being raised with the aim of determining what actions could be implemented to improve the issues.
On completion of the focus group a suitable individual will be nominated to present the outcomes to the senior management team.
5. Action Plans
Nominated personnel from each focus group will be required to formulate a working group which will be chaired by a member of the Senior Management team in order to develop action plans and implement points raised by the Focus Groups. Where points raised by focus groups are not going to be taken forward the Senior Management Team should explain the reason why they are not being undertaken. The Senior Management Team also needs to provide the appropriate resources to allow the action plans to be fully implemented.
6. Review and Feedback
Progress of all the action plans to be posted on company noticeboards. Action plans should be fully reviewed on a monthly basis and where plans are not being achieved appropriate corrective action should be implemented.